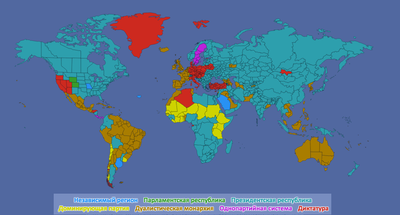
Format e qeverisjes
Forma e qeverisë përcakton karakteristikat e qeverisë, mënyra e ushtrimit të forcës. Në të gjitha format e qeverisë, aty ka një pozicion si një lider (ose diktator), ministër ekonomie (këshilltar ekonomik në diktaturë). Pesë nga format e qeverisjes kanë parlament dhe një pozicion të ministrit të jashtëm.
Contents
Republikë parlamentare
![]() Rrepublika parlamentare - forma bazë e qeverisë/ E gjithë fuqia i takon Parlamentit
Rrepublika parlamentare - forma bazë e qeverisë/ E gjithë fuqia i takon Parlamentit
Republikë presidenciale
![]() Republika presidenciale lind pas zgjedhjeve të liderit në një shtet të sapoformuar.
Republika presidenciale lind pas zgjedhjeve të liderit në një shtet të sapoformuar.
Karakteristikat:
- Zgjedhjet përsëriten çdo 5 ditë.
- Fuqia i takon krijuesve të ligjeve: parlamentit.
Lideri miraton kërkesat për rezidencë, cakton Ministrat, ndryshon ngjyrën e shtetit në hartë, ndryshon himnin dhe urdhërat për qytetarët e shtetit.
- Ligjet mund të pranohen para afatit në rast të 50% + 1 vota PRO.
- Liderat,Guvernatorët dhe Ministrat marin dyfishin e rrogës në gold.
Parti-sunduese
![]() Parti-sunduese - formë qeverisje ku ka vetëm një parti në parlament, ajo që ka marrë shumicën e votave në zgjedhjet parlamentare.
Parti-sunduese - formë qeverisje ku ka vetëm një parti në parlament, ajo që ka marrë shumicën e votave në zgjedhjet parlamentare.
Në këtë rast zgjedhjet përsëriten si zakonisht, çdo 5 ditë.Për të lëvizur te kjo formë qeverisje duhet të kalohet një ligj specifik dhe ky ligj nuk duhet të ketë më pak se 80% vota PRO.
Dictatorship
![]() Dictatorship – form of government where all the power belongs to the leader of the state. As in dominant-party you need a law with 80% of PRO votes passed in parliament. You can only pass dictatorship law from Presidential republic. To move back from dictatorship to the republic you need an action from dictator himself or a successfull revolution in any of the state region.
Dictatorship – form of government where all the power belongs to the leader of the state. As in dominant-party you need a law with 80% of PRO votes passed in parliament. You can only pass dictatorship law from Presidential republic. To move back from dictatorship to the republic you need an action from dictator himself or a successfull revolution in any of the state region.
Features:
- No elections.
- All power belongs to the dictator.
- Majority of laws are passed instantly.
- Dictator has one economic adviser. He can pass economic laws: resources exploration, taxes, buildings upgrades etc. There is no position of foreign minister.
One-party system
![]() One-party system – form of government that has a mixed character, the decision to move from a dictatorship to a one-party system is made by the dictator himself. In this form of government there is only one party in parliament: dictator's party.
One-party system – form of government that has a mixed character, the decision to move from a dictatorship to a one-party system is made by the dictator himself. In this form of government there is only one party in parliament: dictator's party.
Features:
- Immediate transition from dictatorship and back to dictatorship.
- One party in parliament.
- The dictator can instantly pass his laws, but not laws of others.
- No elections.
- No foreign minister.
Executive monarchy
![]() Executive monarchy – form of government that has a mixed character, the decision to move from a dictatorship to an executive monarchy system is made by the dictator himself, as in one-party system. In this form of government parliament plays the role of a council.
Executive monarchy – form of government that has a mixed character, the decision to move from a dictatorship to an executive monarchy system is made by the dictator himself, as in one-party system. In this form of government parliament plays the role of a council.
Features:
- All votes for current bills in the parliament will be removed when the dictator cancels executive monarchy and transfers the state system back to the dictatorship.
- Immediate transition from dictatorship and back to dictatorship.
- Parliament elections.
- Dictator can instantly pass his laws, but not laws of others.
- Parliament can issue bills but they can be only passed if dictator or economy adviser voted for it.
- No foreign minister.